Introduction solar PV modules fault
Solar PV modules, also known as solar panels, are an essential component of solar energy systems. They convert sunlight into electricity, providing a clean and renewable source of power. However, like any other technology, solar PV modules can experience faults or failures that can impact their performance. In this blog post, we will explore the various types of faults or failures that solar PV modules can encounter and their potential effects.
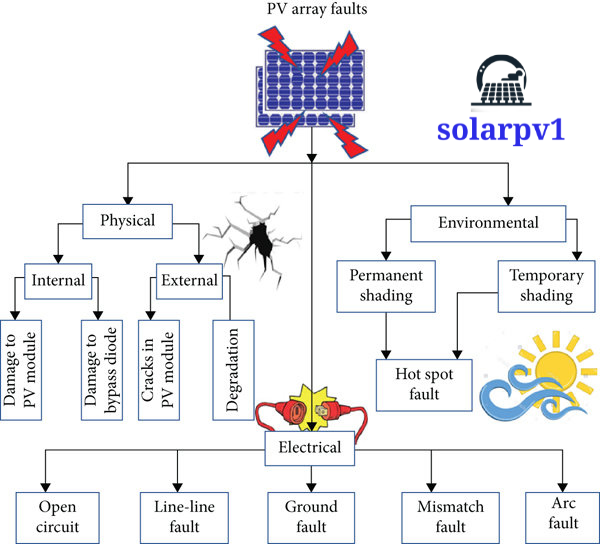
1. Degradation
- Degradation is a common issue that affects the performance of solar PV modules over time. It refers to the gradual decrease in the module’s efficiency and power output. Several factors contribute to degradation, including exposure to sunlight, temperature variations, and environmental conditions.
- One of the main causes of degradation is the presence of microcracks in the solar cells. These microcracks can occur during the manufacturing process or due to mechanical stress. Over time, these cracks can worsen and lead to a decrease in the module’s efficiency.
- Another factor that contributes to degradation is the accumulation of dirt, dust, or other pollutants on the surface of the solar PV module. This reduces the amount of sunlight reaching the solar cells, resulting in decreased power output.
- To minimize degradation, regular maintenance and cleaning of the solar PV modules are essential. Additionally, choosing high-quality modules from reputable manufacturers can help mitigate the effects of degradation.
2. Hotspots
- Hotspots are localized areas of excessive heat within a solar PV module. They can occur due to a variety of reasons, including shading, manufacturing defects, or mismatched cells.
- When a solar cell is shaded or partially shaded, it can act as a resistor, causing an increase in temperature. This localized increase in temperature can lead to a hotspot, which can damage the solar cell and reduce the overall performance of the module.
- Manufacturing defects, such as soldering issues or poor cell connections, can also result in hotspots. These defects can create areas of high resistance, leading to localized heating.
- To prevent hotspots, it is crucial to ensure proper installation and wiring of the solar PV modules. Regular monitoring and maintenance can help detect and address any shading issues or manufacturing defects that may contribute to hotspots.
3. PID (Potential-Induced Degradation)
- Potential-Induced Degradation (PID) is a phenomenon that affects the performance of solar PV modules, particularly in humid environments. It occurs when a voltage potential exists between the solar cells and the grounded frame of the module.
- When a voltage potential is present, current can flow through the module, causing a leakage of charge. This leakage can result in a decrease in the module’s power output and efficiency.
- PID can be mitigated by using PID-resistant modules, which are designed to minimize the effects of voltage potential. Additionally, grounding the module properly and ensuring a high-quality installation can help prevent PID.
Final thoughts
- Solar PV modules are susceptible to various types of faults or failures that can impact their performance. Degradation, hotspots, and PID are some of the common issues that can affect the efficiency and power output of solar PV modules.
- Regular maintenance, proper installation, and choosing high-quality modules are essential to minimize the effects of these faults or failures. By addressing these issues, solar PV systems can continue to provide clean and renewable energy for years to come.