Introduction to Renewable Energy Storage
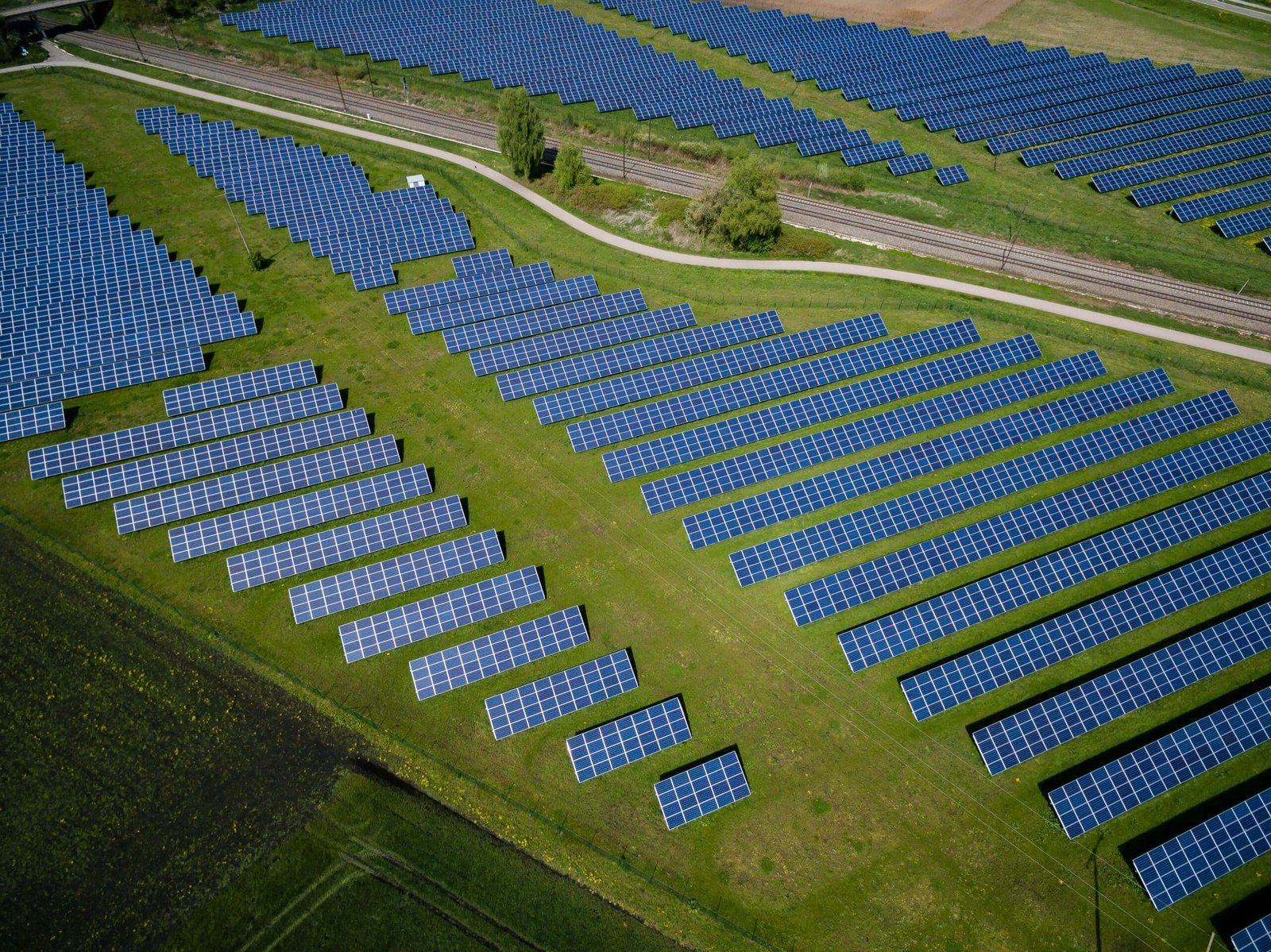
As the world increasingly shifts towards sustainable practices, the prominence of renewable energy storage systems has never been more apparent. These innovative systems serve a critical role in the global energy transition by enhancing the efficiency and reliability of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power. Energy storage technology ensures that the power generated during peak production can be retained for later use, thereby addressing the intermittent nature of these energy sources. This capability is vital for balancing supply and demand, ensuring consumers have access to energy when needed, regardless of generation fluctuations.
The fundamental concept of energy storage revolves around capturing excess energy produced during high generation periods and releasing it during demand surges. This not only optimizes the utilization of renewable resources but also contributes to grid stability. Various storage technologies are available, including batteries, pumped hydro storage, and thermal storage systems, each with its unique advantages and applications. Innovations in these technologies are continually emerging, driven by the need for more efficient, cost-effective solutions that can facilitate the broader use of renewable energy.
Renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, offer significant environmental benefits by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. However, their dependability is closely tied to weather conditions and time of day, which necessitates robust energy storage solutions to mitigate these limitations. Improving the capacity and effectiveness of renewable energy storage is essential for maximizing the potential of these technologies, enabling a smoother integration into the existing energy infrastructure.
In conclusion, the advancement of renewable energy storage systems is essential for fostering a more sustainable energy future. As technology continues to evolve, these systems will play a pivotal role in promoting the reliability and efficiency of renewable energy, ultimately aiding the global shift towards cleaner energy production and consumption.
Current Technologies in Renewable Energy Storage
The evolution of renewable energy storage technologies is crucial in optimizing the utilization of energy generated from sources like solar and wind. A variety of innovative methods are currently being developed that cater to different application needs and efficiency requirements. Among these, mechanical storage systems have garnered significant attention. Notably, pumped hydro storage allows for large-scale energy storage by using excess electricity to pump water uphill to a reservoir. When energy is needed, the water is released to generate hydroelectric power. Though this method offers high capacity and long-term storage, its geographical constraints present limitations in deployment.
Flywheel energy storage is another mechanical solution, where energy is stored in the form of kinetic energy via a rotating mass. This technology is characterized by rapid response times and durability; however, it is less suitable for long-duration energy needs. With both mechanical systems, their scalability and efficiency make them viable options for integrating into the renewable energy grid.
Thermal energy storage is also pivotal, with molten salt being a prominent example. This technology captures excess heat generated during peak sunlight hours, which can later be converted into electricity during lower-generation periods. The reliability and high storage capacity of molten salt make it a key player in solar thermal plants. However, it is essential to consider that the overall efficiency may be reduced during the heat transfer process.
Emerging battery technologies are increasingly reshaping the landscape of renewable energy storage. Lithium-ion batteries, widely used for their high energy density and efficiency, are commonplace in various applications ranging from electric vehicles to grid storage. Solid-state batteries and flow batteries are also gaining traction, promising better safety, longevity, and scalability. Each technology, while presenting unique advantages, also faces limitations, including factors such as cost, resource availability, and energy density. As research continues to advance, these innovations are crucial for facilitating a sustainable energy future.
Innovations on the Horizon
The landscape of renewable energy storage systems is witnessing unprecedented innovations aimed at enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and performance. As the demand for renewable energy surges globally, researchers and engineers are exploring new frontiers in energy storage technology. A notable area of focus is the development of advanced battery materials. Traditional lithium-ion batteries are being critically evaluated, leading to promising alternatives such as solid-state batteries. These batteries can potentially offer greater energy density, improved safety, and longer life cycles, thus revolutionizing how we store renewable energy.
Moreover, researchers are investigating novel approaches to thermal storage systems. Phase change materials (PCMs) are becoming increasingly significant, as they can store and release thermal energy during phase transitions. This innovation enables renewable energy sources such as solar and wind to deliver consistent power, regardless of natural fluctuations. The integration of PCMs facilitates a more stable and reliable energy supply, which is essential for a future heavily reliant on renewable sources.
Additionally, the potential of hydrogen as an energy carrier is gaining traction. Hydrogen can be generated through electrolysis, using excess renewable energy during periods of low demand. Once produced, hydrogen can be stored for later use in fuel cells or even be converted back to electricity. This versatility positions hydrogen as a vital component in achieving energy resilience, particularly in sectors that are hard to electrify, such as heavy transportation and industrial applications.
The implications of these innovations in renewable energy storage systems are profound. They not only promise to enhance the efficiency and longevity of energy storage but also contribute significantly to the broader goal of achieving sustainable and reliable energy systems. As research continues and these technologies mature, they may play a crucial role in transforming the renewable energy landscape, ensuring a cleaner and more sustainable future.
Challenges and the Future of Energy Storage
The renewable energy storage sector faces numerous challenges that impact its growth and effectiveness in addressing the global energy transition. One significant hurdle is economic feasibility. While the costs of renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind, continue to decline, the financial viability of advanced energy storage systems remains a concern. High initial capital costs for technologies like lithium-ion batteries and pumped hydro storage can deter investment, particularly in developing economies where budget constraints are prevalent.
Scalability presents another challenge for renewable energy storage systems. As the demand for energy increases, the ability to scale up storage solutions rapidly becomes critical. Current technologies may not be adequate to meet this increasing need, and development of scalable alternatives, such as solid-state batteries or innovative grid-scale options, is essential. Additionally, environmental impacts associated with the production and lifecycle of energy storage materials—such as lithium extraction—raise concerns about sustainability and ecological balance.
Policy and regulatory issues further complicate the landscape for renewable energy storage. Inconsistent regulations, lack of supportive frameworks, and inadequate incentives can hinder the development and deployment of energy storage solutions. Policymakers need to work collaboratively across sectors to create coherent strategies that promote the integration of storage into the energy mix. Moreover, fostering public-private partnerships can enhance research and innovation, enabling a pathway for transformative storage technologies.
Looking to the future, energy storage markets are expected to see significant growth, driven by the accelerating transition to a low-carbon economy. Investment opportunities abound in developing efficient storage systems and integrating them with smart grid technologies. As countries set ambitious sustainability goals, energy storage will play a pivotal role in balancing supply and demand, facilitating the expansion of renewable energy sources, and ultimately contributing to a resilient and sustainable energy future.