The Solar Power Duck Curve: Understanding the Fluctuations in Solar Energy Generation
Solar power has emerged as a popular and sustainable source of energy in recent years. With its numerous benefits, including reduced carbon emissions and lower operating costs, solar energy has gained significant traction in the global energy landscape. However, one of the challenges associated with solar power is its intermittent nature, which is reflected in what is known as the “solar power duck curve.”
What is the Solar Power Duck Curve?
The solar power duck curve refers to a graphical representation of the difference between electricity demand and the amount of solar energy being generated over the course of a day. The curve gets its name from its resemblance to the shape of a duck, with a steep decline in the morning and a sharp rise in the evening, creating a significant dip in the middle of the day.
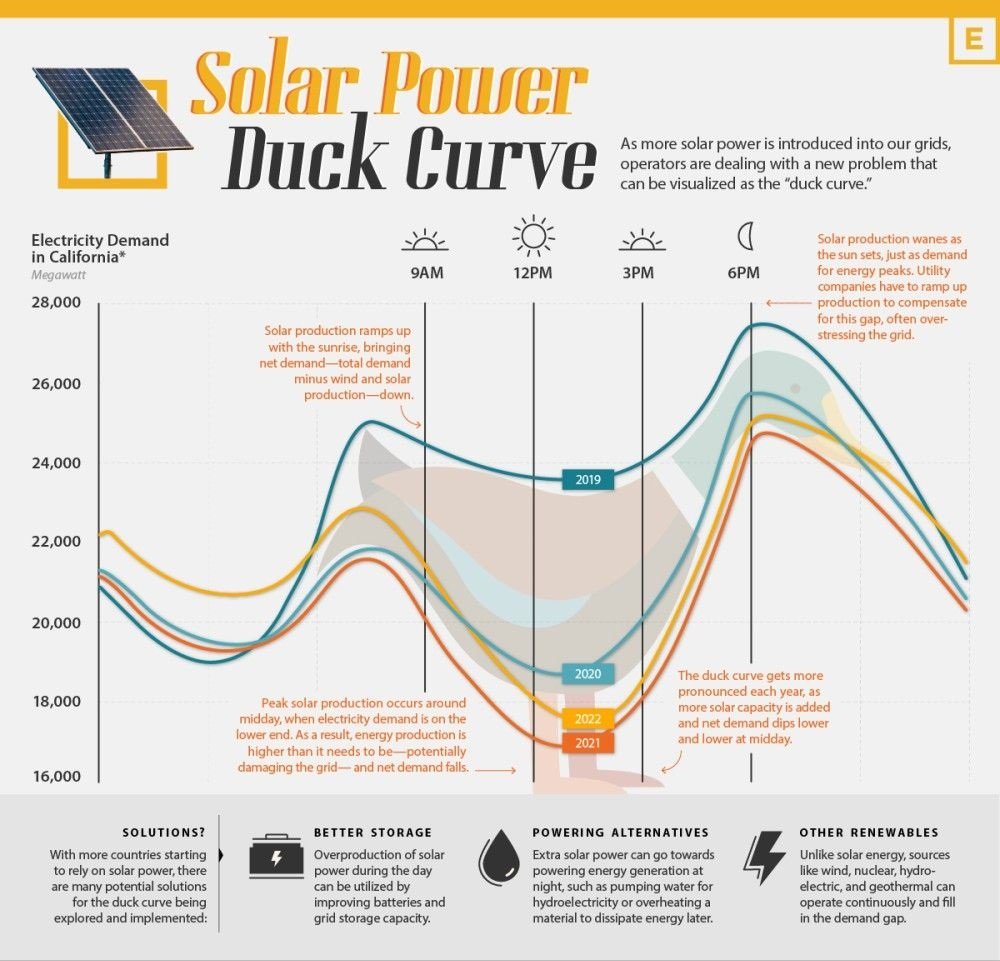
This curve is primarily observed in regions with a high penetration of solar energy, where the midday solar generation exceeds the electricity demand. As a result, the excess solar energy is either wasted or needs to be stored for later use.
Causes of the Solar Power Duck Curve
Several factors contribute to the formation of the solar power duck curve:
- Daytime Electricity Demand: The demand for electricity typically peaks in the morning and evening when people are waking up or returning home from work. This leads to a lower demand during the midday hours when solar energy generation is at its highest.
- Solar Energy Generation: Solar panels produce the most energy during the middle of the day when the sun is at its peak. This leads to an oversupply of solar energy during these hours, causing the curve to dip.
- Limited Energy Storage: While advancements in energy storage technologies have been made, the ability to store excess solar energy for later use is still limited. This means that the excess energy generated during the day cannot be effectively utilized during the peak demand hours in the morning and evening.
Implications and Solutions
The solar power duck curve presents both challenges and opportunities for the solar energy industry. Understanding its implications is crucial for developing effective solutions:
1. Grid Stability: The significant fluctuations in solar energy generation can pose challenges to grid stability. The sudden drop and subsequent rise in energy supply require grid operators to balance the grid in real-time to ensure a reliable electricity supply.
2. Energy Storage: To address the issue of excess solar energy during midday hours, energy storage systems such as batteries can be utilized. These systems allow for the storage of excess energy generated during the day, which can then be discharged during peak demand hours, evening out the fluctuations in energy supply.
3. Demand Response Programs: Another solution is the implementation of demand response programs, which incentivize consumers to shift their electricity usage to times when solar energy generation is high. This helps to align electricity demand with solar energy supply, reducing the need for energy storage and optimizing the utilization of solar power.
4. Time-of-Use Pricing: Time-of-use pricing is a strategy that involves charging different electricity rates based on the time of day. By implementing higher rates during peak demand hours, consumers are encouraged to reduce their electricity usage during these periods, further aligning demand with solar energy generation.
5. Integration with Other Renewable Sources: Integrating solar power with other renewable energy sources, such as wind or hydroelectric power, can help mitigate the fluctuations in energy supply. By diversifying the renewable energy mix, a more consistent and reliable energy supply can be achieved.
The Future of the Solar Power Duck Curve
As solar energy continues to grow and evolve, the solar power duck curve is expected to become more prevalent. However, advancements in energy storage technologies and grid management systems are likely to address the challenges posed by this curve.
With ongoing research and innovation, the solar power duck curve can be effectively managed, ensuring the efficient utilization of solar energy and a more stable and sustainable electricity grid.