Introduction to Solar Panels Work
- Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, have become a cornerstone of modern renewable energy solutions. These devices harness the power of sunlight, converting it into electricity that can be used to power homes, businesses, and even entire communities. The basic principle behind solar panels is the photovoltaic effect, a process where certain materials generate an electric current when exposed to sunlight. This technology has seen significant advancements over the years, making it a viable and popular choice for residential energy needs.
- One of the most compelling reasons for the growing popularity of solar panels in residential settings is their environmental impact. As a renewable energy source, solar panels contribute to a significant reduction in carbon footprints. Unlike fossil fuels, which release harmful greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, solar energy is clean and sustainable. By opting for solar power, homeowners can play a crucial role in combating climate change and promoting environmental sustainability.
- In addition to their environmental benefits, solar panels offer substantial financial advantages. The initial investment in solar technology may seem daunting to some, but the long-term savings are considerable. Homeowners can reduce or even eliminate their electricity bills, depending on the size of their solar system and energy consumption. Furthermore, many governments and local authorities offer incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and grants to encourage the adoption of solar energy, making it more accessible and affordable for the average homeowner.
- The increased accessibility and affordability of solar technology have also contributed to its rise in popularity. Advances in manufacturing processes and economies of scale have driven down the costs of solar panels and related equipment. Additionally, the introduction of various financing options, including solar leases and power purchase agreements (PPAs), has made it easier for homeowners to invest in solar energy without bearing the full upfront cost.
- Overall, solar panels represent a forward-thinking energy solution that aligns with both environmental and economic goals. As technology continues to evolve, the adoption of solar energy in residential settings is expected to accelerate, paving the way for a more sustainable and cost-effective future.
The Science Behind Solar Panels
- Solar panels harness the power of the sun to generate electricity, a process rooted in the principles of the photovoltaic (PV) effect. At the heart of this technology are solar cells, which are typically composed of semiconductor materials such as silicon. These solar cells are the fundamental building blocks of solar panels and play a crucial role in converting sunlight into usable electrical energy.
- When sunlight, which is composed of tiny particles called photons, strikes the surface of a solar cell, the energy from these photons is absorbed by the semiconductor material. This absorption of energy excites the electrons within the material, causing them to break free from their atoms. When these free electrons are set into motion, they create an electric current. This phenomenon, known as the PV effect, is the cornerstone of how solar panels generate electricity.
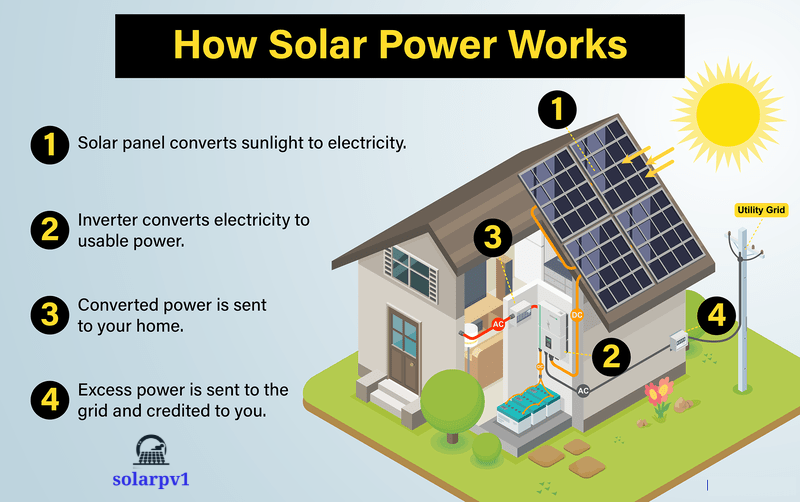
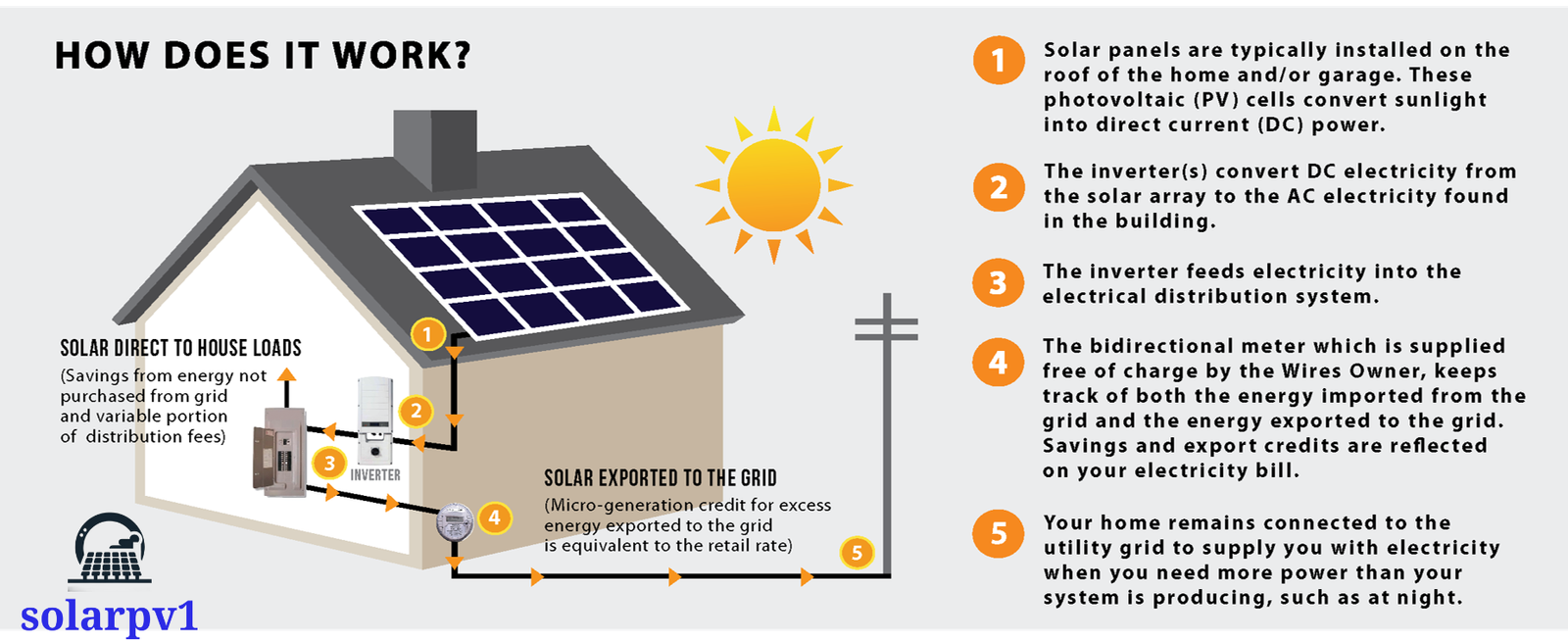
- A solar panel system is made up of several key components, each serving a specific function to ensure the efficient conversion and utilization of solar energy. The most visible component is the solar panel itself, which is an assembly of multiple solar cells interconnected to form a cohesive unit. These panels are typically mounted on rooftops or other structures using specialized mounting systems designed to optimize exposure to sunlight.
- The electricity generated by the solar cells is in the form of direct current (DC). However, most household appliances and the electrical grid operate on alternating current (AC). To bridge this gap, a crucial component known as the inverter is used. The inverter converts the DC electricity produced by the solar panels into AC electricity, making it compatible with household appliances and the grid.
- Overall, the science behind solar panels is a fascinating interplay of physics and engineering, enabling the transformation of sunlight into a reliable and sustainable source of electricity for residential use. By understanding these technical underpinnings, homeowners can better appreciate the incredible potential of solar energy and its role in shaping a greener future.
- Installation Process and Requirements
- The installation of solar panels on a house involves a systematic process that ensures optimal performance and compliance with local regulations. The initial phase is an assessment and planning stage, which includes a comprehensive site evaluation and shading analysis. This stage is crucial as it determines the viability of the solar installation. A professional installer will inspect the roof condition, orientation, and angle to ensure it is suitable for maximum energy absorption. Additionally, they will conduct a shading analysis to identify any potential obstructions that could impede sunlight exposure, such as trees or neighboring buildings.
- System sizing is another critical aspect of the planning phase. The installer will calculate the household’s energy needs and design a system that meets these requirements. This involves determining the number of solar panels required and their optimal placement. Once the planning phase is complete, the actual installation process can begin.
- The installation process starts with mounting the solar panels onto the roof. This involves attaching mounting brackets to the roof, which securely hold the solar panels in place. The panels are then fixed onto these brackets. It is essential that the roof is structurally sound and capable of supporting the additional weight of the panels.
- Following the mounting of the panels, the next step is the electrical wiring. The solar panels are connected in series or parallel configurations, depending on the system design. These connections are then linked to an inverter, which converts the direct current (DC) generated by the panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used by the household. The inverter is connected to the home’s electrical panel, integrating the solar power into the existing electrical grid.
- Securing necessary permits and scheduling inspections are integral parts of the installation process. Local building codes and regulations must be adhered to, and this often entails obtaining permits from local authorities. After installation, a thorough inspection is typically required to ensure the system is installed correctly and safely.
- Roof suitability and orientation are also significant considerations. A south-facing roof with minimal shading is ideal for solar panel installation. However, east or west-facing roofs can also be effective, though they may require additional panels to meet energy needs. The roof’s condition should be assessed to confirm it can withstand the installation and operation of solar panels over their lifespan.
- In conclusion, the installation of solar panels on a house is a detailed process that includes careful planning, structural assessments, and adherence to local regulations. By following these steps, homeowners can ensure a successful and efficient transition to solar energy.
Benefits and Maintenance of Residential Solar Panels
- Installing solar panels on a home offers numerous advantages that make it an attractive investment for many homeowners. One of the primary benefits is the significant reduction in energy costs. By generating electricity from sunlight, homeowners can reduce their reliance on the grid and ultimately lower their monthly utility bills. In some cases, surplus energy can even be sold back to the grid, providing an additional source of income.
- Beyond financial savings, residential solar panels contribute positively to the environment. Solar energy is a renewable resource, meaning it does not deplete natural resources or produce harmful emissions. By opting for solar power, homeowners can reduce their carbon footprint and help combat climate change. This shift towards sustainable energy also decreases the overall demand for fossil fuels, promoting a cleaner and healthier environment.
- Moreover, many governments and local authorities offer tax incentives, rebates, and other financial incentives to encourage the adoption of solar energy. These incentives can significantly reduce the initial installation costs, making solar panels a more affordable option for many homeowners. It is crucial to research and understand the available incentives in your area to maximize the financial benefits of your solar investment.
- While the benefits of solar panels are clear, maintaining their efficiency and longevity requires regular upkeep. Homeowners should ensure their solar panels are kept clean and free from debris, as dirt and grime can reduce their efficiency. It is recommended to clean the panels at least twice a year, or more frequently if you live in an area with heavy pollution or dust.
- Monitoring the performance of your solar panel system is also essential. Many systems come with monitoring software that allows homeowners to track energy production and detect any issues early on. Regularly checking this data ensures your system is operating at its optimal capacity and can help identify problems such as panel degradation or inverter failures.
- Addressing potential issues promptly is critical to maintaining the overall efficiency of your solar panel system. Inverter failures, for example, can significantly impact energy production and should be repaired or replaced as soon as possible. Additionally, keeping an eye on the condition of the panels themselves can help prevent long-term degradation and ensure they continue to perform effectively.
- To maximize your solar investment, consider scheduling periodic professional inspections. These inspections can identify any hidden issues and provide peace of mind that your system is functioning correctly. By combining regular maintenance, monitoring, and professional support, homeowners can ensure their solar panels remain a valuable and efficient energy source for years to come.