Understanding the Specific Yield of a Solar System
When it comes to solar energy, one of the key factors to consider is the specific yield of a solar system. The specific yield refers to the amount of energy that a solar system can produce under specific conditions. It is an important metric that helps determine the efficiency and effectiveness of a solar installation.
What is Specific Yield?
- The specific yield of a solar system is the amount of electricity that can be generated by a solar panel or a solar array, typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), under specific conditions. These conditions include factors such as the location of the solar system, the angle and orientation of the solar panels, the efficiency of the panels, and the amount of sunlight available.
- The specific yield is an important metric because it helps determine the potential energy output of a solar system. By understanding the specific yield, solar system designers and installers can optimize the system’s performance and ensure that it meets the energy needs of the user.
Factors Affecting Specific Yield
Several factors can influence the specific yield of a solar system. These factors include:
1. Location: The geographical location of a solar system plays a crucial role in determining its specific yield. Areas with more sunlight throughout the year will generally have a higher specific yield compared to regions with less sunshine.
2. Angle and Orientation: The angle and orientation of the solar panels also impact the specific yield. Ideally, solar panels should be tilted at an angle that maximizes their exposure to the sun. The orientation of the panels, whether they face south, east, or west, can also affect the specific yield.
3. Efficiency: The efficiency of the solar panels themselves is another important factor. Higher efficiency panels can convert a greater percentage of sunlight into electricity, resulting in a higher specific yield.
4. Shading: Shading from trees, buildings, or other obstructions can significantly reduce the specific yield of a solar system. It is essential to ensure that the solar panels are installed in an area where they receive maximum sunlight throughout the day.
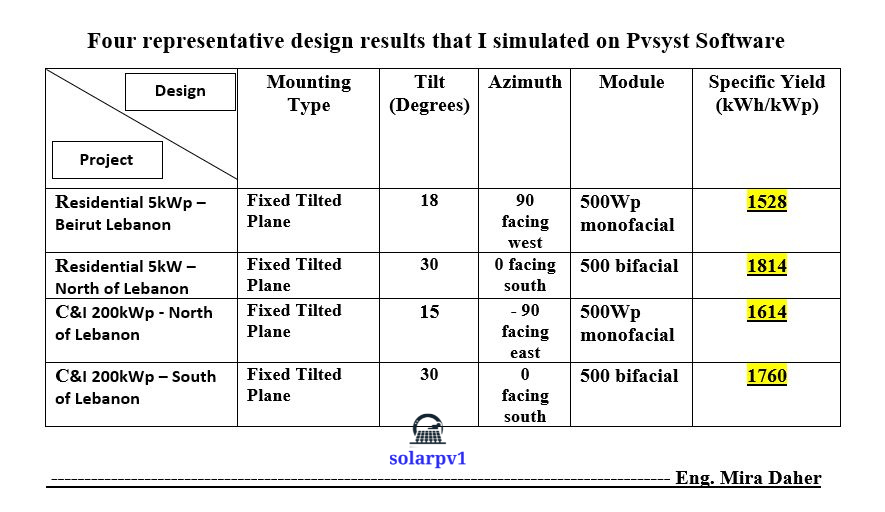
Calculating Specific Yield
The specific yield of a solar system can be calculated by multiplying the peak power rating of the solar panels by the number of hours of sunlight received in a day. The formula for calculating specific yield is as follows:
Specific Yield (kWh) = Peak Power Rating (kW) x Hours of Sunlight
For example, if a solar system has a peak power rating of 5 kW and receives an average of 5 hours of sunlight per day, the specific yield would be:
Specific Yield = 5 kW x 5 hours = 25 kWh
It is important to note that the specific yield may vary throughout the year due to seasonal changes in sunlight availability. Therefore, it is crucial to consider the average specific yield over an extended period to get a more accurate estimate of a solar system’s performance.
Importance of Specific Yield
The specific yield of a solar system is essential for several reasons:
1. System Sizing: By knowing the specific yield, solar system designers can accurately determine the number of solar panels required to meet the energy needs of a user. This helps in optimizing the system size and ensuring that it produces enough electricity to offset the user’s energy consumption.
2. Financial Analysis: The specific yield is also crucial for financial analysis, such as calculating the return on investment (ROI) of a solar system. It helps estimate the amount of electricity that can be generated and the potential savings on energy bills.
3. Performance Monitoring: Monitoring the specific yield of a solar system over time allows users to track its performance and identify any issues or inefficiencies. It helps in identifying maintenance needs and optimizing the system’s performance.
Final Thoughts
The specific yield of a solar system is a critical metric that determines the energy output of a solar installation. By considering factors such as location, angle, orientation, efficiency, and shading, the specific yield can be optimized to ensure maximum energy production. Understanding the specific yield helps in system sizing, financial analysis, and performance monitoring, ultimately enabling users to harness the full potential of solar energy.
