Understanding PERC Technology in Solar Panels
Solar energy has become an increasingly popular and viable source of renewable energy in recent years. As technology continues to advance, solar panels have become more efficient at converting sunlight into electricity. One of the key advancements in solar panel technology is PERC (Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell) technology. In this blog post, we will explore what PERC technology is and how it works.
What is PERC Technology?
PERC technology is a design modification that improves the efficiency of solar panels. Traditional solar cells have a simple structure where light enters the front surface of the cell and is absorbed by the semiconductor material. The absorbed light then generates electrons, creating an electric current. However, a significant amount of light energy is lost as heat in this process.
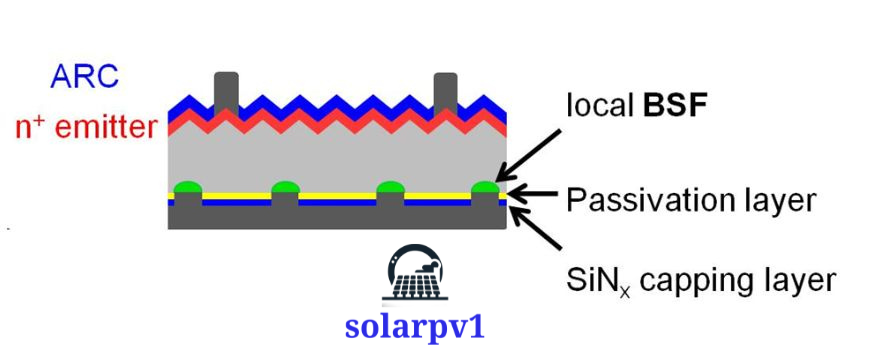
PERC technology addresses this issue by adding a passivation layer to the rear surface of the solar cell. This layer helps to reduce the recombination of electrons and positively charged holes, allowing more electrons to flow through the cell and generate electricity. By minimizing energy losses, PERC technology significantly improves the overall efficiency of solar panels.
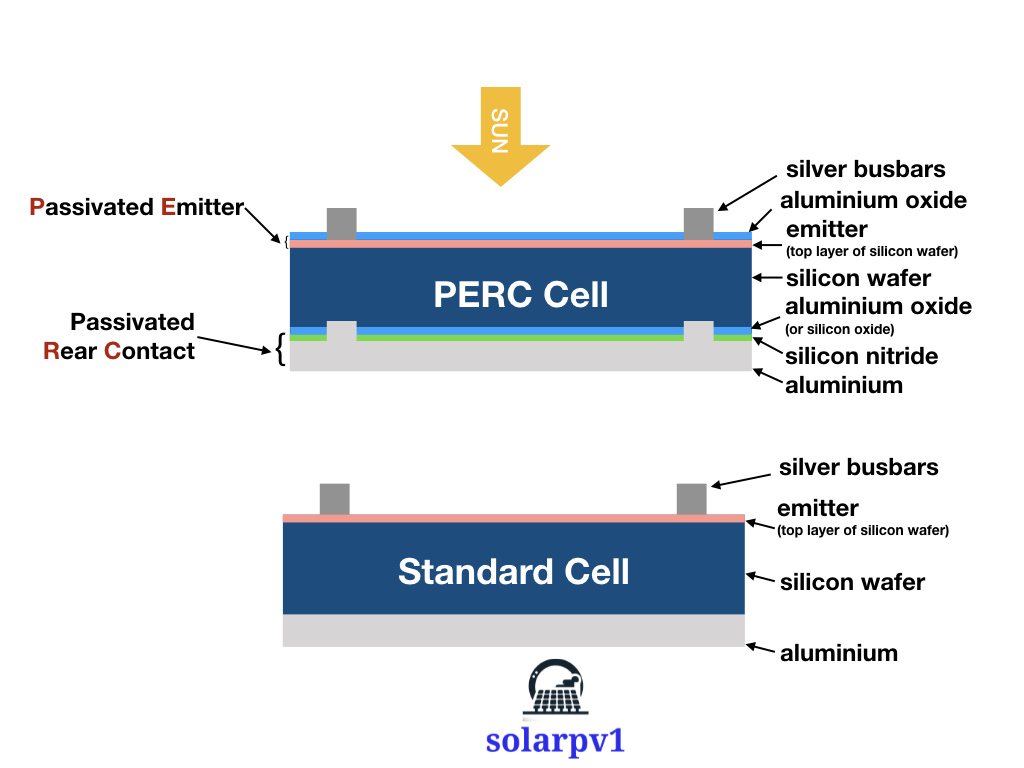
How Does PERC Technology Work?
The implementation of PERC technology involves several key steps:
- Texturing: The front surface of the solar cell is textured to reduce the amount of light reflected back into the atmosphere. This texturing process increases the surface area of the cell, allowing for more efficient light absorption.
- Emitter Formation: A layer of dopant material is added to the front surface of the solar cell to create an emitter. This layer helps to generate a strong electric field that separates the photo-generated electrons and holes.
- Passivation Layer: A passivation layer is applied to the rear surface of the solar cell. This layer helps to reduce the recombination of electrons and holes, allowing for better electron flow and improved cell efficiency.
- Back Surface Field: A layer of conductive material is added to the rear surface of the cell to create a back surface field. This field helps to further enhance the electric field and improve the overall performance of the solar cell.
- Metal Contacts: Metal contacts are added to the front and rear surfaces of the solar cell to allow for the collection of electric current.
By combining these steps, PERC technology enables solar panels to achieve higher conversion efficiencies compared to traditional solar cell designs. The passivation layer plays a crucial role in reducing energy losses and improving the overall performance of the solar panel.
Benefits of PERC Technology
PERC technology offers several advantages over traditional solar cell designs:
- Higher Efficiency: PERC technology improves the conversion efficiency of solar panels, allowing for more electricity to be generated from the same amount of sunlight.
- Better Low-Light Performance: PERC technology enhances the ability of solar panels to generate electricity in low-light conditions, such as cloudy days or early mornings/evenings.
- Improved Temperature Coefficient: PERC technology reduces the negative impact of high temperatures on solar panel performance, ensuring better efficiency even in hot climates.
- Enhanced Durability: The passivation layer in PERC solar cells helps to protect the underlying semiconductor material, increasing the longevity and durability of the solar panel.
- Compatibility: PERC technology can be easily integrated into existing solar panel manufacturing processes, making it a cost-effective and scalable solution.
Final Thoughts
PERC technology is a significant advancement in solar panel design that improves the efficiency and performance of solar panels. By adding a passivation layer to the rear surface of the solar cell, PERC technology reduces energy losses and enhances the flow of electrons, resulting in higher conversion efficiencies. With its numerous benefits, PERC technology is helping to drive the adoption of solar energy as a sustainable and reliable source of power.
