Lifespan of solar panels
- Solar panels have emerged as a pivotal technology in the global shift towards renewable energy. At their core, solar panels are devices designed to convert sunlight into electricity, harnessing the abundant energy of the sun. This conversion is primarily facilitated by photovoltaic (PV) cells, which are the fundamental building blocks of a solar panel. These cells are typically made of silicon and work on the principle of the photovoltaic effect, where sunlight photons knock electrons loose from atoms, generating a flow of electricity.
- A complete solar panel system consists of several key components. Besides the photovoltaic cells, an inverter is crucial as it converts the direct current (DC) produced by the PV cells into alternating current (AC), which is the standard electricity used in homes and businesses. Additionally, mounting systems are essential for securing the panels in place, either on rooftops or ground installations, ensuring they are positioned optimally to capture the maximum amount of sunlight.
- The push towards solar energy is not just a trend but a necessary step in addressing climate change and energy sustainability. One of the most significant benefits of solar panels is the reduction in electricity bills. By generating their own power, homeowners and businesses can drastically cut down on their dependence on the grid, leading to substantial savings over time. Moreover, solar panels contribute to lowering carbon footprints, as they produce clean, green energy without emitting greenhouse gases.
- Another attractive advantage of installing solar panels is the potential increase in property value. Homes equipped with solar systems are often more appealing to buyers who are looking for energy-efficient properties. Furthermore, various government incentives and rebates can make the initial investment in solar technology more affordable, providing an added financial benefit.
- Overall, the adoption of solar panels is a win-win for both individuals and the environment. As technology advances and costs decrease, solar panels are becoming a more accessible and practical solution for sustainable energy production.
Cost Analysis of Solar Panels
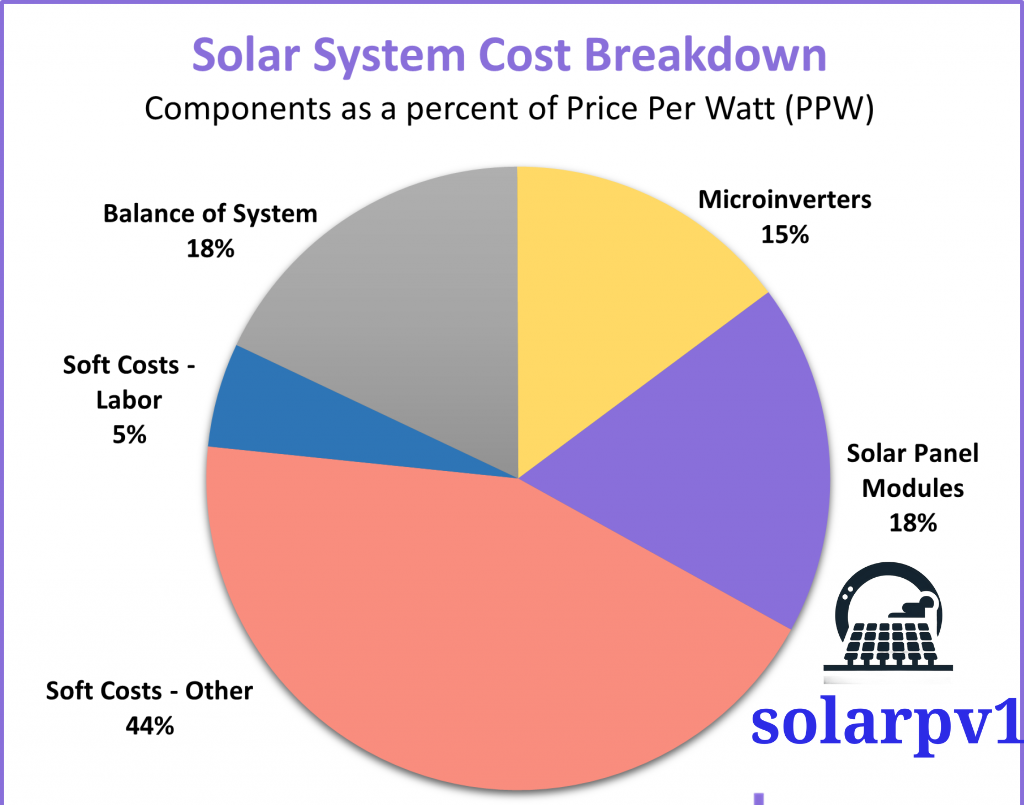
- The cost of solar panels is influenced by a range of factors, which can be broadly categorized into equipment costs, installation expenses, and additional expenditures. Equipment costs typically include the solar panels themselves, inverters, and mounting hardware. High-efficiency panels and advanced inverters can increase the upfront cost but may offer better long-term savings. On average, residential solar panel systems can range from $15,000 to $25,000, while commercial installations might cost between $50,000 and $200,000, depending on the scale and complexity.
- Installation costs encompass labor, permits, and inspections. Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of the installation. Permits and inspections are mandatory to ensure compliance with local regulations, adding to the overall expense. These costs typically account for 10-20% of the total installation cost.
- Additional expenses include maintenance and energy storage solutions such as batteries. While maintenance costs are generally low, it is essential to factor in periodic cleaning and potential repairs. Batteries for energy storage can significantly increase the initial investment but provide the benefit of energy independence and reliability. Battery systems can add anywhere from $5,000 to $10,000 to the total cost.
- Government incentives, tax credits, and rebates play a crucial role in reducing the net cost of solar panels. The Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) allows homeowners and businesses to deduct a significant percentage of their solar installation costs from their federal taxes. State and local incentives further reduce the financial burden, making solar energy more accessible.
- Financing options like solar loans, leases, and Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) provide flexibility in managing the financial commitment. Solar loans enable property owners to spread the cost over several years, often with low-interest rates. Leases and PPAs allow users to install solar panels with little to no upfront cost, paying for the energy produced instead. These options make solar energy a viable solution for a broader audience, promoting sustainable energy adoption.
Factors Influencing the Lifespan of Solar Panels
- The typical lifespan of solar panels ranges between 25 to 30 years, though this can be influenced by various factors. One of the primary determinants of a solar panel’s longevity is the quality and material used in its construction. High-quality materials and superior manufacturing processes generally result in panels that last longer and perform more efficiently over time. For instance, monocrystalline panels, known for their high efficiency and durability, often outlast polycrystalline and thin-film panels.
- Weather conditions also play a significant role in the lifespan of solar panels. Panels are designed to withstand diverse environmental stresses, but extreme conditions can accelerate their degradation. Hail, heavy snowfall, and extreme temperatures can physically damage the panels or impair their efficiency. Proper installation can mitigate some of these effects. For instance, ensuring that panels are securely mounted and angled correctly can prevent snow buildup and reduce wind-related damage.
- Maintenance is another critical factor. Regular cleaning to remove dirt, leaves, and other debris ensures that panels receive maximum sunlight and operate at peak efficiency. Checking for and promptly addressing any physical damage or electrical issues can also prolong their lifespan. Even minor issues, if left unattended, can escalate and lead to more significant problems.
- The degradation rate of solar panels is an essential concept to understand, as it affects their efficiency over time. On average, solar panels degrade at a rate of about 0.5% to 1% per year. This means that after 25 years, a panel might operate at around 75% to 87.5% of its original capacity. The degradation rate can vary based on the type of solar panels: monocrystalline panels typically degrade more slowly than polycrystalline and thin-film panels.
- In comparing different types of solar panels, monocrystalline panels generally offer the longest lifespan and the highest efficiency, making them a preferred choice for long-term investments. Polycrystalline panels, while less efficient and slightly more prone to degradation, are often more affordable. Thin-film panels, despite their flexibility and lightweight nature, usually have the shortest lifespan and the highest degradation rates.
Maximizing the Lifespan and Value of Your Solar Investment
- Ensuring the longevity and value of your solar panel investment involves a combination of regular maintenance, monitoring, and protective measures. Proper care can significantly extend the lifespan of your solar panels, enhancing their performance and financial returns.
- One of the most critical aspects of solar panel maintenance is keeping the panels clean. Dust, dirt, and debris can accumulate on the surface of the panels, reducing their ability to absorb sunlight efficiently. Regular cleaning, at least twice a year, is essential. This can be done using a soft brush and water, or by hiring professional cleaning services to ensure thoroughness and prevent potential damage.
- In addition to cleaning, regular inspections are crucial. Checking for physical damage, such as cracks or scratches, can prevent minor issues from escalating. Ensure that all electrical connections are secure and functioning correctly. Loose connections can lead to energy loss or more severe electrical problems. Professional maintenance services can provide comprehensive inspections and repairs, ensuring your system operates optimally.
- Another valuable investment is in monitoring systems that track the performance of your solar panels. These systems can provide real-time data on energy production and alert you to any anomalies that may indicate underlying issues. By addressing problems promptly, you can maintain peak efficiency and prolong the lifespan of your panels.
- Protecting your solar panels from potential hazards is also vital. Physical damage can occur due to extreme weather conditions, falling debris, or shading from overgrown trees or nearby buildings. Regularly trimming trees and ensuring that structures do not cast shadows on the panels will maximize their exposure to sunlight and enhance energy production.
- At the end of their useful life, solar panels still have value. Many components can be recycled or repurposed, reducing environmental impact and recovering some of your investment. Recycling programs are available through various manufacturers and specialized companies, ensuring that valuable materials are not wasted.
- By implementing these strategies, you can maximize the lifespan and value of your solar panel investment, ensuring efficient energy production and financial savings for many years to come.